New analysis signifies the solar’s magnetic box originates just about the outside and now not deep inside the megastar, . This upends many years of prevailing medical idea that positioned the sector greater than 130,000 miles underneath the outside of the solar. It additionally brings us nearer to working out the character of the solar’s magnetic box, which has been on scientist’s minds since Galileo.
The learn about, and a group of world researchers, means that the magnetic box if truth be told generates 20,000 miles underneath the outside. This used to be found out after the group ran a sequence of advanced calculations on a NASA supercomputer. It’s value noting that those are simply preliminary findings and extra analysis is needed to substantiate the knowledge.
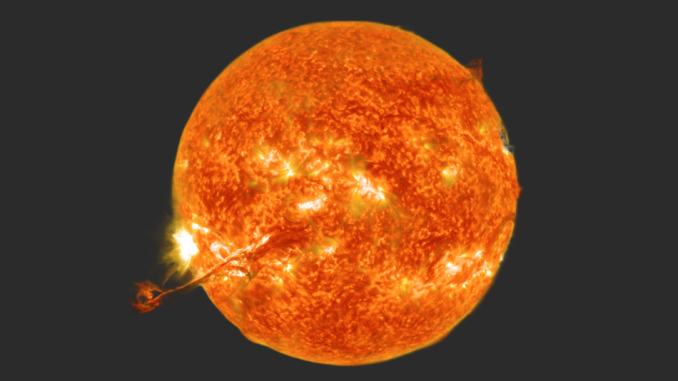
The solar’s magnetic box fluctuates in a cycle that lasts 11 years. All the way through the most powerful a part of this cycle, tough winds and sunspots shape on the sun equator, along side plumes of subject matter that motive the right here on Earth. Earlier theories that position the magnetic box deeper inside the solar have had a troublesome time connecting those quite a lot of sun phenomena. Scientists hope that, given additional learn about, they’ll be capable of use this concept not to handiest give an explanation for the advent of sun occasions, however extra appropriately expect when they are going to happen.
Every 2nd, 1.5 million heaps of sun subject matter, touring at 100 miles according to 2nd, shoot off the solar. Earth’s magnetic box deflects maximum of it, however now not all. The sun wind, a circulate of charged debris, flows at 447 km/s (1 million mph), and whilst the magnetic box protects… pic.twitter.com/40CSNZYesU
— Ancient Vids (@historyinmemes) January 1, 2024
This might result in extra than simply previous predictions of the following aurora borealis match. The solar’s intense magnetic power may be the supply of sun flares and eruptions of plasma known as coronal mass ejections. When those ejections go back and forth towards Earth, a wide variety of dangerous issues occur. This famously befell again in 1859, when an enormous geomagnetic typhoon created the most important sun typhoon in recorded historical past.
That is , attributed to British astronomer Richard Christopher Carrington. The sun flare, which used to be if truth be told a magnetic explosion at the solar’s floor, in short outshone the solar and led to coloured lighting to erupt all over the place the planet, very similar to the aurora borealis. It additionally supercharged telegraph cables, stunning operators, and set telegraph paper on fireplace. It used to be beautiful nasty.
Now, this used to be 1859, prior to the fashionable use of electrical energy and prior to computer systems and all similar applied sciences. If one thing just like the Carrington Match had been to happen these days, . The emitted X-rays and ultraviolet mild would intrude with electronics, radio and satellite tv for pc alerts. The development would motive a sun radiation typhoon, which might be fatal to astronauts now not totally supplied with protecting equipment.
It will additionally lead a coronal mass ejection to bump up in opposition to Earth’s magnetic box, which , mobile phone satellites, trendy automobiles or even airplanes. The ensuing international energy outages may just final for months. Closing month’s smallish (slightly talking) typhoon and that used to be no Carrington-sized match. Even worse? We’re completely due for this to occur. It’s mainly a ticking time bomb.
So those findings may just, in concept, be used to arrange new early caution strategies for large-scale sun flares hitting Earth. In the future, we may have sun flare warnings along storm warnings and the like. The analysis has already demonstrated some fascinating hyperlinks between sunspots and the solar’s magnetic job.
“We still don’t understand the sun well enough to make accurate predictions” of sun climate, lead learn about writer Geoffrey Vasil of the College of Edinburgh . Those new findings “will be an important step toward finally resolving” this mysterious procedure, of Northwestern College.
This text comprises associate hyperlinks; should you click on this kind of hyperlink and make a purchase order, we would possibly earn a fee.

Leave a Reply